BAL Spotlights Series
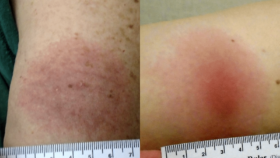
 Anna Schotthoefer, PhD, a project scientist at Marshfield Clinic Research Institute in Wisconsin, discusses the collection and analysis of a specific subset of blood and urine samples for Lyme Disease Biobank—a Bay Area Lyme Foundation program—from patients diagnosed with tick-borne diseases in the state. Marshfield Clinic serves a large population in Wisconsin and Michigan’s Upper Peninsula, which are highly endemic for Lyme disease. Her Bay Area Lyme-funded study of the Marshfield samples focused on visual documentation of rashes associated with Lyme disease and the challenges in accurately diagnosing the disease based on these rashes. The results highlight the difficulties in recognizing early Lyme: only two of 69 patients presented with the classic bullseye rash that doctors learn is the gold standard for diagnosing Lyme from textbooks. Schotthoefer discusses the variety of different rashes that can result from a tick bite, the characterization of the spectrum of rashes, the need for better Lyme diagnostics, and the ongoing efforts to develop new testing methods using the samples collected in LDB. She expresses optimism that in the next five to ten years, there will be significant advancements in Lyme disease detection, diagnosis, and therapeutics—largely thanks to patients who have contributed samples to LDB for ongoing research.
Anna Schotthoefer, PhD, a project scientist at Marshfield Clinic Research Institute in Wisconsin, discusses the collection and analysis of a specific subset of blood and urine samples for Lyme Disease Biobank—a Bay Area Lyme Foundation program—from patients diagnosed with tick-borne diseases in the state. Marshfield Clinic serves a large population in Wisconsin and Michigan’s Upper Peninsula, which are highly endemic for Lyme disease. Her Bay Area Lyme-funded study of the Marshfield samples focused on visual documentation of rashes associated with Lyme disease and the challenges in accurately diagnosing the disease based on these rashes. The results highlight the difficulties in recognizing early Lyme: only two of 69 patients presented with the classic bullseye rash that doctors learn is the gold standard for diagnosing Lyme from textbooks. Schotthoefer discusses the variety of different rashes that can result from a tick bite, the characterization of the spectrum of rashes, the need for better Lyme diagnostics, and the ongoing efforts to develop new testing methods using the samples collected in LDB. She expresses optimism that in the next five to ten years, there will be significant advancements in Lyme disease detection, diagnosis, and therapeutics—largely thanks to patients who have contributed samples to LDB for ongoing research.
“The textbooks doctors read in medical school tell them, ‘Look for a bullseye rash; look for the target-like lesion,’ and it turns out that’s wrong. There is a need to continue educating clinicians and providers that Lyme rashes are a spectrum.”
– Anna Schotthoefer, PhD
 Sunday, August 26th is
Sunday, August 26th is